Forms of the Letter Lām: The Arabic letter Lām (ل) is considered one of the fundamental and easily recognizable letters in the Arabic alphabet. It is characterized by its fluidity and simplicity in both pronunciation and writing. Despite its apparent simplicity, the forms of the letter Lām vary depending on its position within a word. Therefore, learners must practice its different shapes to master accurate reading and writing. In this lesson, we will explore the various forms of the letter Lām when it appears at the beginning, middle, and end of a word—both in connected and isolated forms—along with practical examples that support comprehension and application.
Interactive Activities to Teach the Forms of the Letter Lām
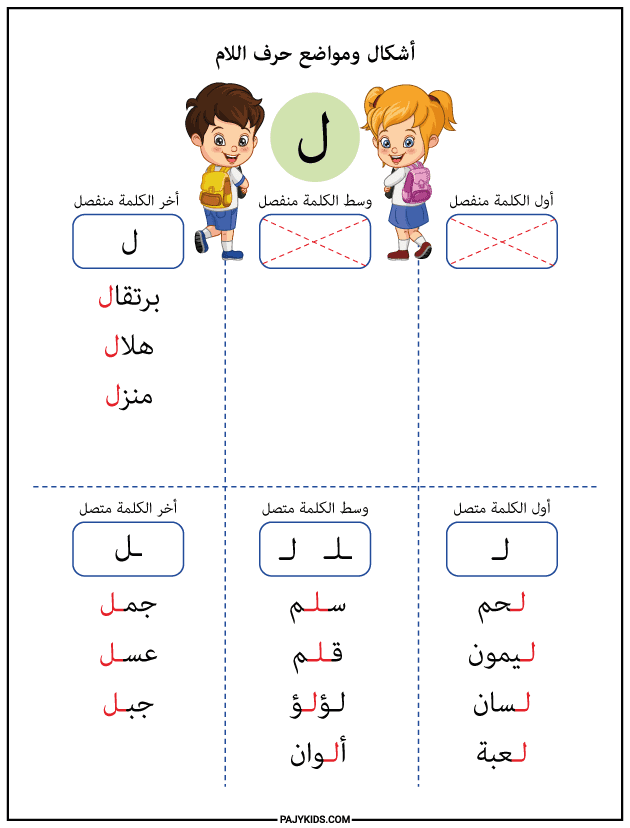
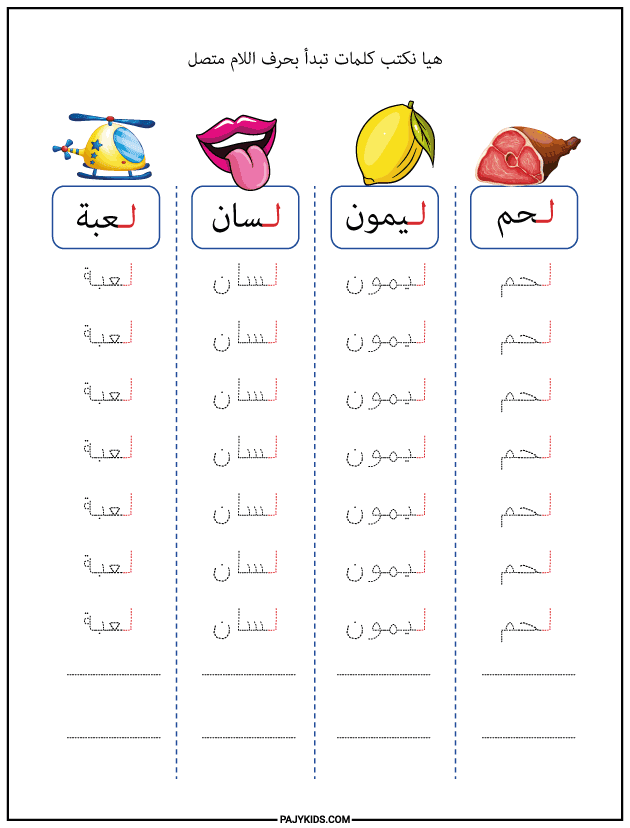
- Form of the Letter Lām at the Beginning of a Word
When Lām appears at the beginning of a word, it connects only to the letter that follows and is written as: “لـ”.
Examples: Lemon (ليمون), Toy (لعبة), Tongue (لسان), Gentle (لطيف), Color (لون), Meat (لحم), Lemon (ليمون).
In this position, the form of the letter Lām begins with a downward curve that extends horizontally toward the next letter. This is one of the most fundamental forms of the letter Lām, which learners should master during the early stages of literacy development.
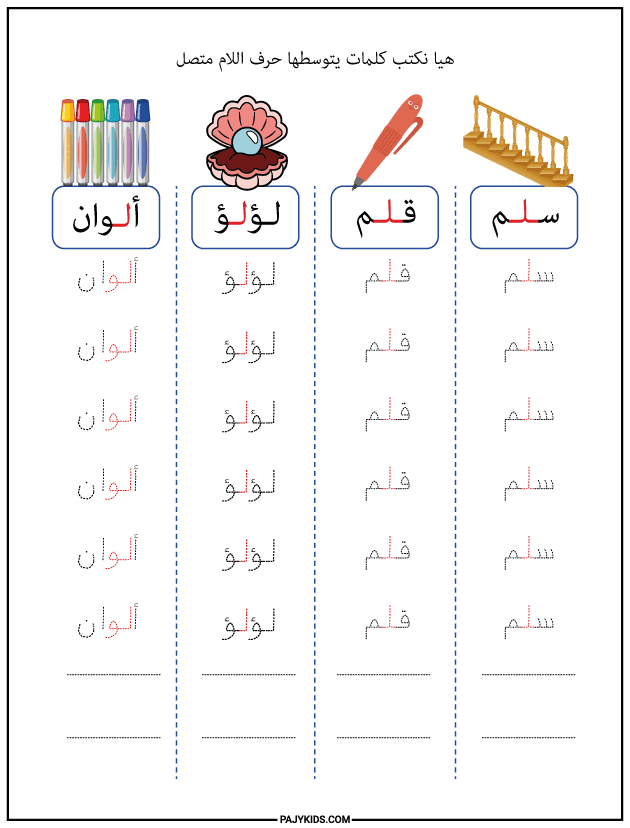
- Form of the Letter Lām in the Middle of a Word
When Lām appears in the middle of a word, it connects to both the preceding and following letters and is written as: “ـلـ”.
Examples: Playground (ملعب), Salad (سلطة), Student (تلميذ), Pen (قلم), Ladder (سلم), Pearl (لؤلؤ), Colors (ألوان).
In this case, the letter blends smoothly into the word while maintaining its clear and simple form. It is essential for students to become proficient in this shape, as it is among the most frequently occurring forms of the letter Lām in daily language use.
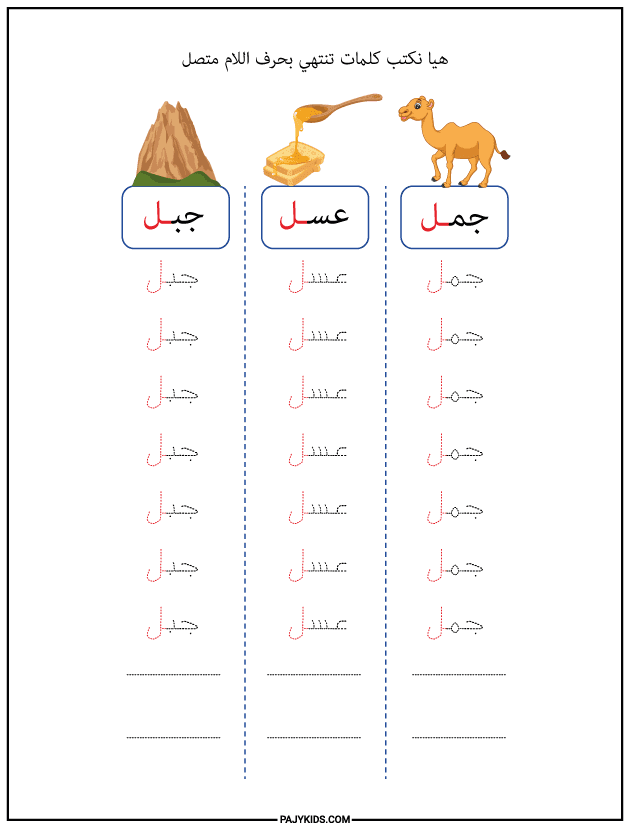
- Form of the Letter Lām at the End of a Word (Connected)
When Lām appears at the end of a word and is connected to the preceding letter, it is written as: “ـل”.
Examples: Camel (جمل), Easy (سهل), Hero (بطل), Bee (نحل), Mountain (جبل), Honey (عسل).
This form extends along the writing line and connects smoothly to the preceding letter, featuring a slight curve at the top. It is one of the important forms of Lām that learners must recognize and distinguish from similar letters in Arabic script.
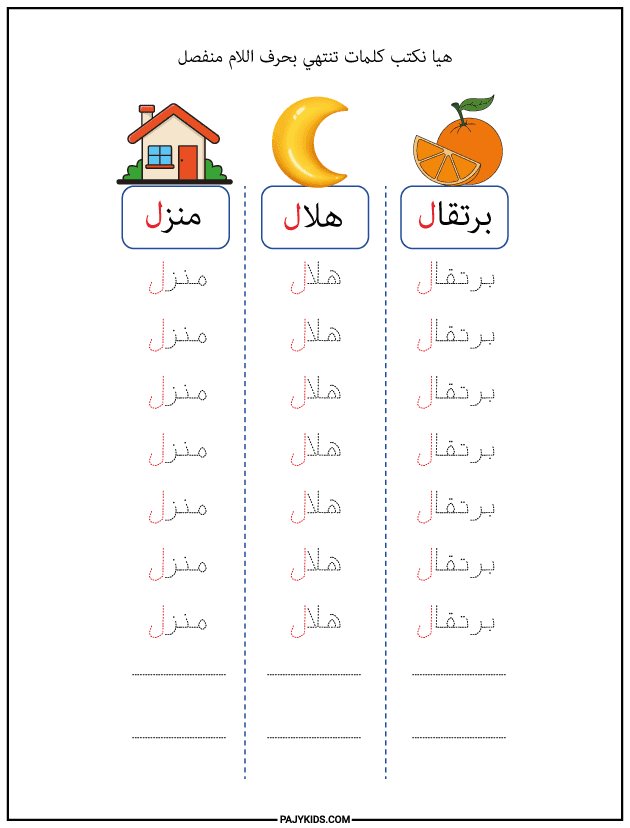
- Form of the Letter Lām at the End of a Word (Isolated)
When Lām appears at the end of a word and is preceded by a non-connecting letter, it is written in its isolated form: “ل”.
Examples: Orange (برتقال), Crescent (هلال), House (منزل).
Although the shape is relatively simple, accurately identifying it helps young learners read with confidence. This is a clear and distinct form of Lām, and it should be emphasized when teaching letter recognition.
Consistent practice of the forms of the letter Lām significantly enhances both reading and writing skills. It also aids in distinguishing between visually similar letters such as Lām (ل) and Kāf (ك). Incorporating practice into daily learning activities, such as copying or word formation, strengthens the learner’s visual memory and understanding of letter shapes. The more diverse and engaging the learning approaches, the more effective and long-lasting the acquisition of these forms becomes.